CODEX 2.2
Please make your selection from the above CODEX menu options for Episode 2.2
KEY-TEXT
Listen to the audio feed from TSTT Mission Control as you read, operatives.
Marcus Cilnius Maecēnās in Pompēiīs habitat. vīllam habet in oppidō. vīlla tablīnum pulchrum habet. Marcus in tablīnō sedet, et cogitat dē avō. Marcus habet librum; in librō est fābula dē Gāiō Cilniō Maecēnāte. Gāius Maecēnās est avus Marcī, sed Gāius Maecēnās est mortuus.
fābula in librō dīcit:
Gāius Cilnius Maecēnās est amīcus principis. Gāius Maecēnās Vergilium et Horātium cognoscit. multam pecūniam habet. populus dīcit, "Gāius Maecēnās lapidem dīvīnum habet." populus dīcit "Lapis dīvīnus pecūniam dat." sed lapidem nōn habet. amīcum habet, et amīcus potentiam dat."
Visual Walkthrough
KEY-TEXT
Prometheus
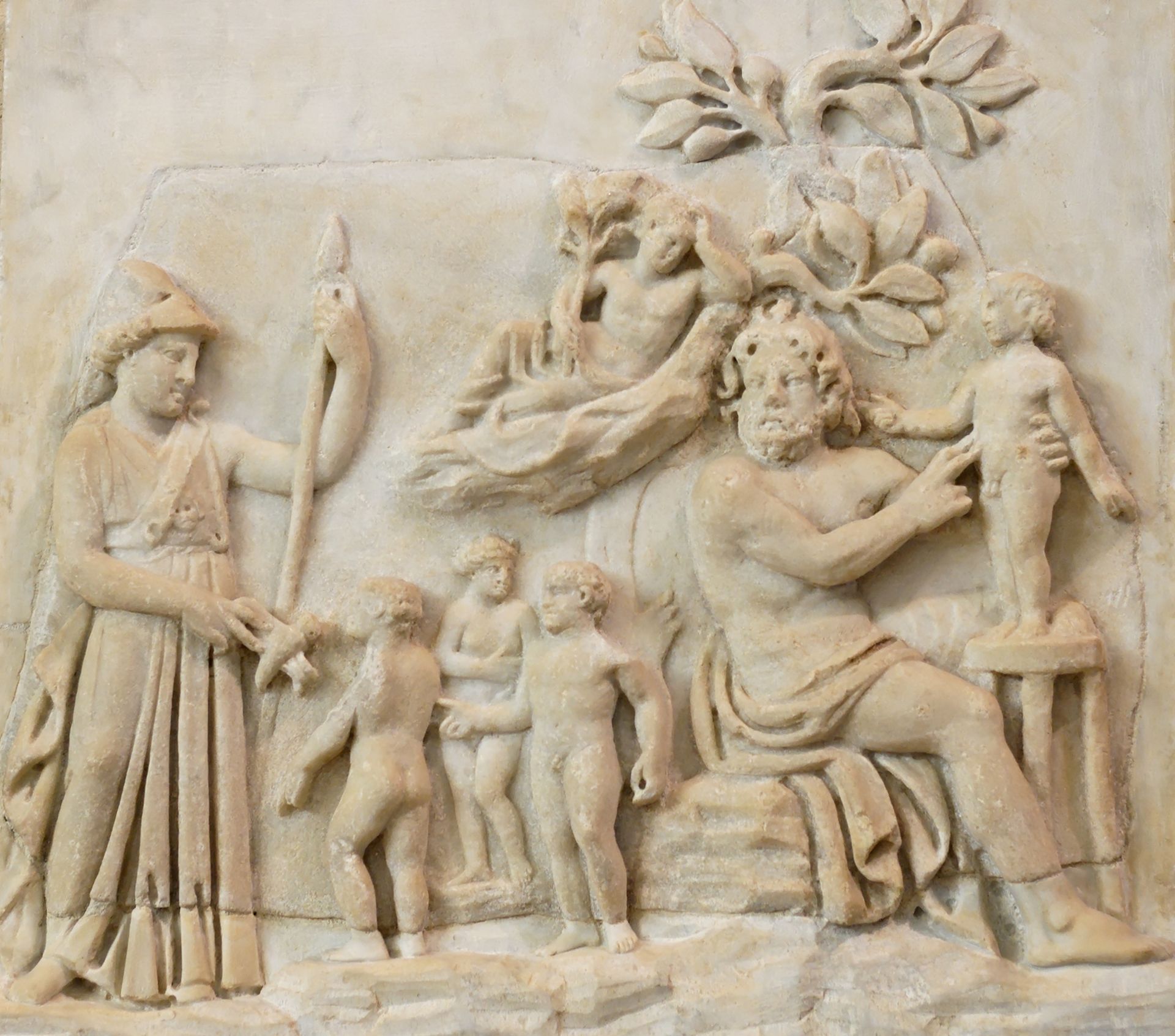

postquam bellum contra Gigantēs, Olympiī Deī totum imperium habent. in terrā multa animālia habitant sed hominēs non iam terram habitant. fortasse maximus deus homines creat aut fortasse Promētheus hominēs ē terrā facit. hī hominēs nunc ad caelum spectant et deōs adorant.
hī hominēs animālia sacrificant sed saepe parvus cibus remanet. Promētheus, fīlius Iapetī, saepe ad hūmānōs spectat et eōs adiuvāre desiderat. Promētheus tunc cōnsilium capit; Promētheus fraudāre Iovem desiderat.
Promētheus sacrificium capit et tunc inīquē dīvidit. ponit ossa in sēbō sed carnem in coriō ponit. ille tunc Iovem vocat et dicit, “necesse est tibi unum sacrificium legere atque alium sacrificium humanīs dāre.”
Iuppiter dolum cognoscit sed tamen ossa in sēbō legit. ille deus dīcit, “Promētheus mē fallit! ita vero, hominēs nunc carnem habent sed… poenam dō!” Iuppiter nunc est iratus et Promētheus est territus. Iuppiter flammās (ignem) ā hominibus capit. hūmānī nunc frigidī sunt nēque hūmānī cēnam coquere nōn possunt.
Promētheus iterum Iovem fallit; ignem in ferulā celat, ā caelō descendit, et ad humanōs flammās portat. hominēs iterum calorem habent et non iam frigidī sunt. hūmānī iterum cēnam coquere possunt.
Iuppiter iterum est iratus. Iuppiter nunc hūmānōs fallit et donum eīs dat…
Word Count: 192
GRAMMATICA
-s
Operative, you may have noticed that every verb you’ve encountered so far has been a third person verb . You have now encountered a second person verb, with the phrase "quid agis?", or “what are you doing?”
Just as in English, Latin can use pronouns to replace nouns. These are referred to as personal pronouns. You have now learned the personal pronoun for “you”: tē.
If you look back at the phrase "quid agis ?", you will notice that it does not include tu. That is because the English word “you” is contained within the verb agis; that is, agis by itself means “you do,” and a separate pronoun is not necessary (although it may be included if the author chooses).
-ō
Operative, in the previous entry you learned about second person verbs. You will now learn about first person verbs, or verbs being performed by the speaker. The Demiurge would like to help you understand the difference by looking at three examples, in which the same event is described by in three different situations:
Caecilius might say to Tiberius, “servus cēnam parat .” - "The slave prepares dinner."
Caecilius might say to the servus, “tū cēnam parās .” - "You prepare dinner."
The servus might say to Caecilius, “ego cēnam parō .” - "I prepare dinner."
You should immediately notice that the ending changes on those three variations of the verb. With all of the singular endings for present verbs in place, operatives should review this video briefing from latintutorial.com:
VERBA
| agis | you do, drive, act | verb |
| excitat | she/he wakes up | verb |
| fortasse | perhaps | adverb |
| habet | she/he has | verb |
| labor / laborem | work, labor, task | noun |
| liber / librum | book | noun |
| locus | place | noun |
| scribit | she/he writes | verb |
| via | road, way, path | noun |
| volumen | scroll | noun |
CULTURALIA
Operatives, you are advised that the TSTT-immersion character Marcus Cilnius Maecenas is the fictional grandson of a very real grandfather, Gaius Cilnius Maecenas. You are advised by the Demiurge to use any knowledge you can acquire about the grandfather in deciding on your actions and your participation in your immersion-missions.
You may wish to consider this short documentary courtesy of Kings and Generals on YouTube about Roman Patronage:
Another thing to consider is that Roman libri were quite different from what we think of as “books.” You are advised to obtain LP additions by using any knowledge you can acquire about libri in acting in the immersion-space of the TSTT. In addition, the Demiurge has secured information courtesy of the University of Michigan about various types of writing materials in the ancient world. It is worth exploring these links for the current mission.
ATTUNEMENT
Directions: Using the CULTURALIA section of your CODEX as a guide, answer the following questions:
1.For what is Maecenas most famous?
2.From the list below, circle the names of the artists that Maecenas assisted.
Vergil Petronius Horace Propertius Catullus
3. Identify two of the artists whose names you circled.
4. What is the difference between a liber and a volūmen?
5. How did a Roman writer use a tabula cēra?
2.2.a
Directions: Choose the correct form for the word in the parentheses. Then translate the sentence.
1. (Sextus, Sextum) Recentium excitat.
2. (Recentium, Recentius) in vīllā est.
3. labor (Recentius, Recentium) exspectat.
4. Sextus (liber, librum) dēsīderat.
5. (vīlla, vīllam) in oppidō est.
6. (malum, malus) est in vīllā.
7. Marcus est (malus, malum).
8. Marcus (liber, librum) habet.
2.2.b
Directions: Choose the correct form for the word in the parentheses. Then translate the sentence.
1. Caecilius Tiberium (excitās, excitat, excitō).
2. Tiberius Caeciliō (dīcō, dīcis, dīcit), “quid (agit, agis)?
3. Caecilus (dīcō, dīcit, dīcis), “(dēsīderās, dēsīderō, dēsīderat) librum.”
4. Caecilus rogat coquum, “(coquitnē, coquisnē, coquōnē) cēnam?”
5. coquus respondet, “ita vērō. cēnam (coquis, coquit, coquō).”
2.2 KEY-TEXT Comprehension Questions
Directions: Using the KEY-TEXT section of your CODEX as a guide, answer the following questions:
1. ubi Marcus Cilnius Maecēnas habitat?
2. quid agit Marcus Cilnius Maecēnas in tablīnō?
3. quid in librō est?
4. estne Gāius Maecēnas pater Marcī aut avus Marcī?
5. quem Gāius habet amīcum?
6. cognoscitne Vergilium et Horatium?
7. quid Gāius habet?
8. quid nōn habet?
9. quid populus dīcit?
10. quid amīcus Gāiī Maecēnatis dat?
2.2 KEY-TEXT B (PROMETHEUS) Comprehension Questions
Directions: Using the KEY-TEXT B section of your CODEX as a guide, answer the following questions:
1. According to the story, in what two ways were humans created?
2. What was the problem with sacrificing animals to the gods?
3. Jupiter is forced to choose between two options; what are they and which option seems to be the logical choice?
4. What option does Jupiter pick and why?
5. What is Jupiter’s punishment for Prometheus’ trick? Why is this punishment severe?
6. How does Prometheus trick Jupiter again?