Tab
Please make your selection from the above CODEX menu options for Episode 11.1
KEY-TEXT
Listen to the audio feed from TSTT Mission Control as you read, operatives.
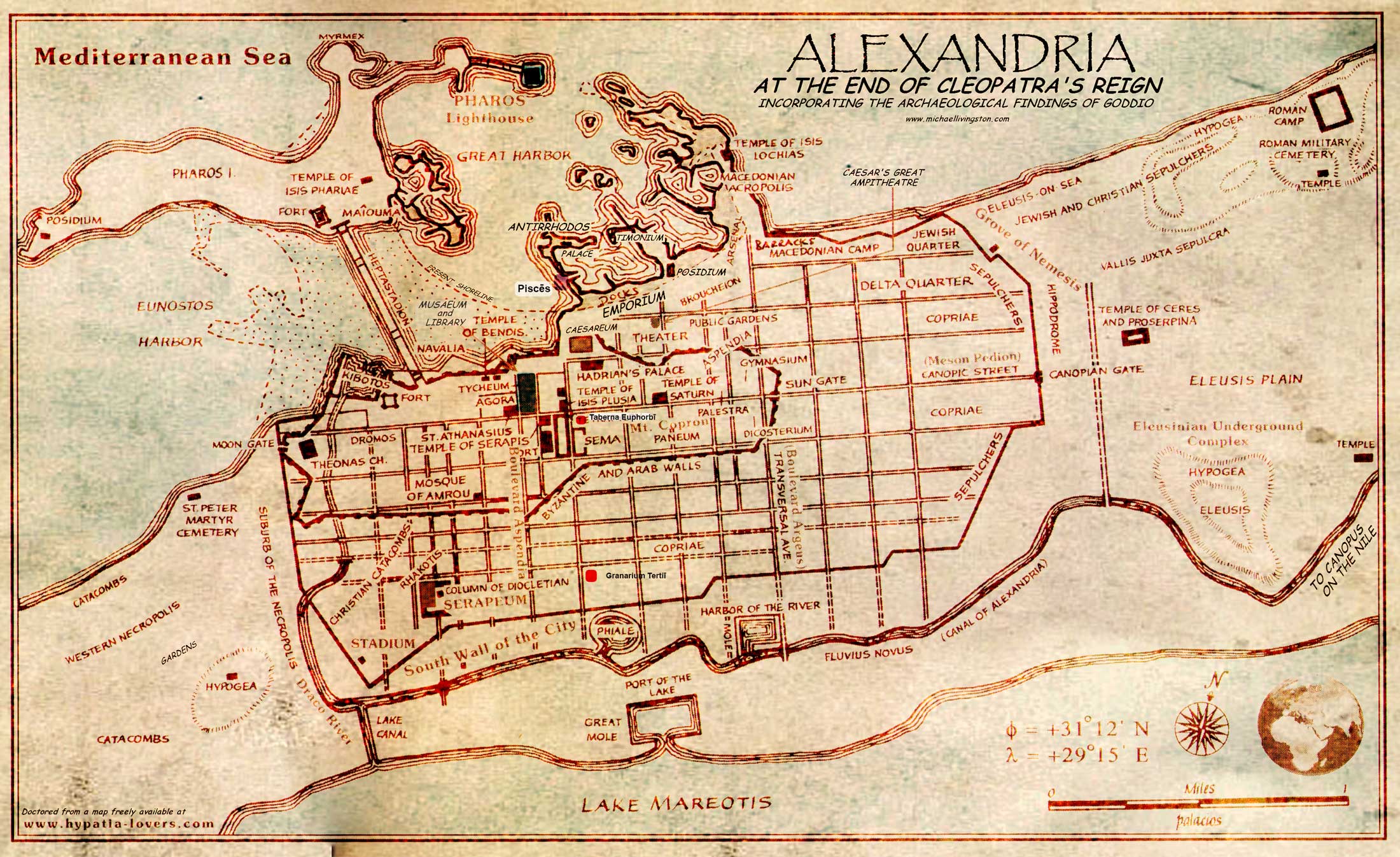
taberna Euphorbī
postquam Caecilius Euphorbum līberāverat, īit Brundisium et ad Aegyptum navigāvit. duō tīrōnēs, quōs Marcus Brundisium mīserat, Euphorbum in nāve conspēxērunt. illī quoque ad Aegyptum nāvigāvērunt et eum spectāvērunt antequam Marcus eum spectāvit. Marcus Maecēnās diū servum Caeciliī cupīverat quod Euphorbus cēram Caeciliī habēbat.
dum nāvigābat, Euphorbus mercātōrī Aegyptiō, quī volēbat tabernam vendere, occurrit. taberna, quae in Alexandrīā fuit, erat parva, sed erat grāta Rōmānīs Graecīsque. taberna Aegyptiōs, quī omnēs Rōmānōs ōdērunt, nōn dēlectāvit. diū Euphorbus dē tabernā putāverat et tandem cōnstituit tabernam mercātōris in Alexandrīā emere quod multam pecūniam servāvit dum prō Caeciliō labōrāverat.
itaque Euphorbus ad tabernam suam novam vīsitāvit et erat laetus. multōs post diēs ianuās aperuit. prīmum nēmō advēnerat sed mox multī Rōmānī Graecīque tabernam novam Euphorbī intrābant. Euphorbus erat occupātus cotīdiē.
{slider Visual Walkthrough color="green"|closed}
GRAMMATICA
Singular: -ae, -ī, -is
Plural: -ārum, -ōrum, -um
Operatives, we now should turn our attention to the final of our five standard case endings: the genitive. While we recognize that term is not at all helpful, you can think of the genitive as being primarily the possessive case. We express this in english with the little word "of" or an 's. Consider the following:
vīlla Marcī erat māgna.
The house of Marcus was large.
Marcus' house was large.
ānulus Octāviānae est aēneus.
The ring of Octaviana is bronze.
Octaviana's ring is bronze.
Mīlitēs Lapidis populum servant.
The Soldiers of the Stone protect the people.
Consider all of the genitive endings:
| 1st Declension | 2nd Declension | 3rd Declension | |
| singular | villae | servī | Lapidis |
| plural | villārum | servōrum | Lapidum |
For an overview of the genitive, please review this video briefing from latintutorial.com.
VERBA
CULTURALIA
ATTUNEMENT
Directions: Using the key-text for 11.1, answer the following questions in complete Latin sentences.
1. quō ivit Euphorbus? quō nāvigāvit?
2. quid voluit mercātor quī Euphorbō occurrit?
3. eratne taberna grāta Graecīs Rōmānīsque?
4. quid ēgit Euphorbus dē tabernā?
5. quī advēnerat prīmum? quī advēnerant mox?
Directions: Refer back to the key-text in 11.1 to complete the following:
Find and copy:
a. 5 prepositional phrases
b. 6 verbs in the pluperfect tense
c. 11 nouns in the accusative singular
d. 10 verbs in the perfect tense
e. 2 nouns in the dative case
f. 7 adjectives
CULTURALIA Comprehension Questions
Directions: Using the CULTURALIA for 10.1, answer the following questions.
dē Pharō
1. What was the Pharos of Alexandria? When was it built and how tall was it?
2. Who comissioned the construction of the Pharos? Under whom was it finally finished? How long did it take to complete?
3. Describe the placement and the construction of the Pharos. Why do you think that the site was chosen?
4. How was the Pharos ultimately destroyed?
dē Alexandriā
1. When was Alexandria built and who founded it?
2. Why is the location of Alexandria important? How did this impact the development of the intellectual and cultural status of the city?
3. What three cultures were at the center of activity in Alexandria? Does this suprise you?
4. How did the ancient people deal with the problem of three distinct groups coexisting in the city? Was it successful?
5. Would a solution like that work in today's world in a city with many cultures coexisting? Why or why not?