Tab
Please make your selection from the above CODEX menu options for Episode 4.1
KEY-TEXT
Listen to the audio feed from TSTT Mission Control as you read, operatives.
mālum pulcherrimae
ōlim deī deaeque convīvium habēbant. Discordiam nōn invitāvērunt et illa dea erat īrātissima. Discordia in mālō 'PULCHERRIMAE' scrīpsit et mālum in convīvium iēcit. Iūnō et Venus et Minerva mālum dēsīderābant. Iuppiter dīxit, "ego cōnstituere nōn possum. mortālis Paris dēbet cōnstituere." Paris mālum Venerī dedit et Venus pulcherrimam fēminam mortālem, Helēnam, Paridī dedit. sed ēheu! Helēna iam erat marīta.
{slider Visual Walkthrough color="green"|closed}
KEY-TEXT
Mālum Aureum
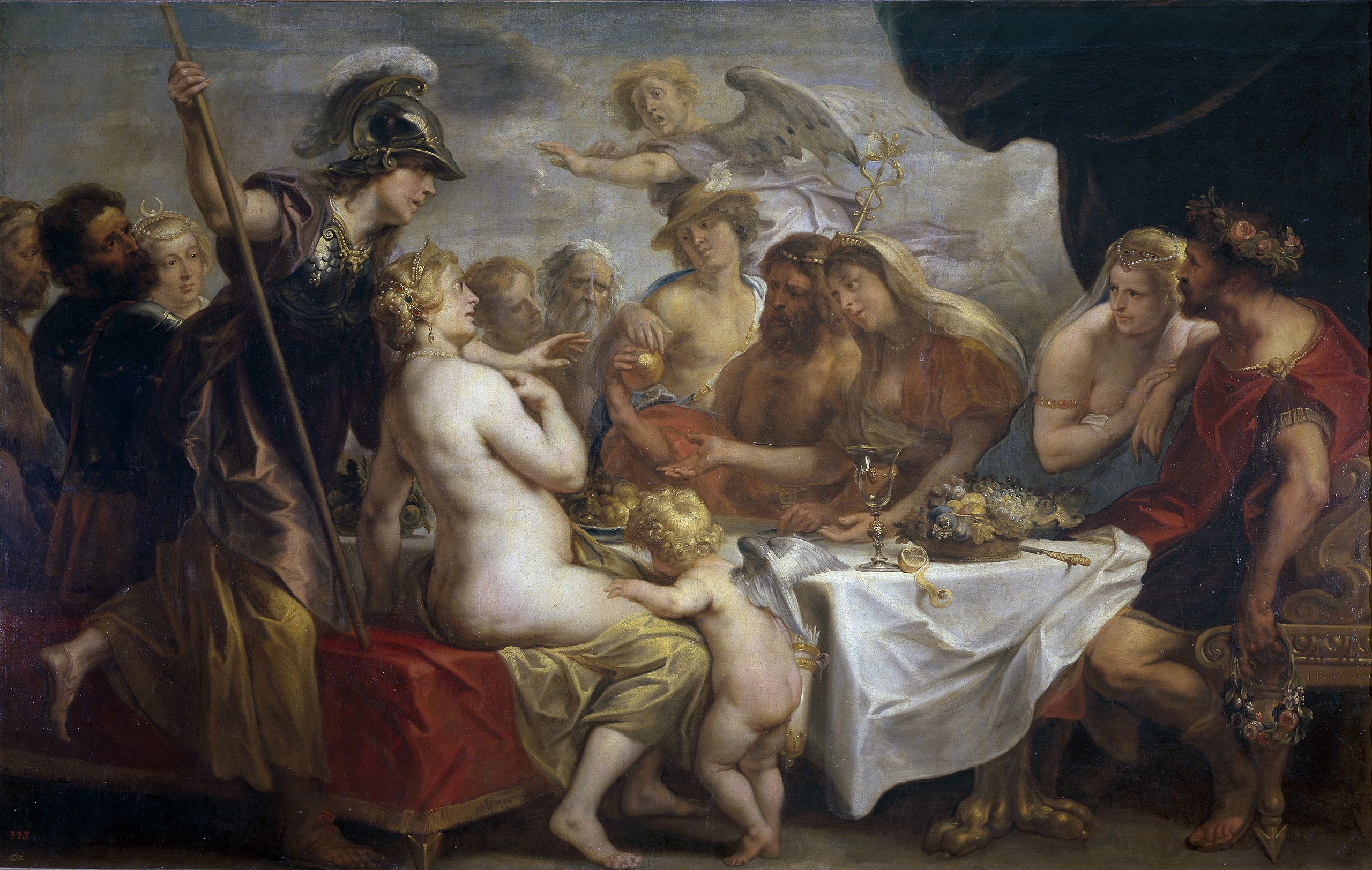

ōlim deī deaeque convīvium habēbant. hērōs Pēleus voluit in mātrimōnium deam Thetidem ducere.
deī Discordiam nōn invitāvērunt et illa dea erat īrātissima. Discordia cōnflīctiōnem amāvit.
Discordia in mālō 'PULCHERRIMAE' scrīpsit et mālum in convīvium iēcit. Iūnō et Venus et Minerva mālum dēsīderābant. Iuppiter dīxit, "ego cōnstituere nōn possum. mortālis Paris dēbet cōnstituere." atque Iuppiter mortālem Paridem ad convīvium vōcāvit. Paris erat fīlius Priamī, rēgis Trōiae.
Iūnō Paridī dīxit, “possum dāre tibi regnum Asiae Eurōpaeque.”
Minerva Paridī dīxit, “possum dāre tibi sapientiam et artem in proeliō.”
Venus Paridī dīxit, “possum dāre tibi pulcherrimam fēminam mortālem.”
erat difficile Paridī cōnstituere et ille longē putāvit. Paris dēsīderāvit omnia quae deae eī dāre voluērunt.
Paris tandem mālum Venerī dedit et Venus pulcherrimam fēminam mortālem, Helēnam, Paridī dedit. Iūnō et Minerva erant īrātissimae quod eīs Paris mālum nōn dedit.
sed ēheu! Helēna iam erat marīta. marītus Helēnae erat Menelaus, rēx Spartae.  postquam multōs annōs, Paris ad Spartam nāvigāvit et Menelaum Helēnamque vīsitabat. Menelaus in hospitiō Paridem accēpit et Helēna Paridī multa dōna dedit.
postquam multōs annōs, Paris ad Spartam nāvigāvit et Menelaum Helēnamque vīsitabat. Menelaus in hospitiō Paridem accēpit et Helēna Paridī multa dōna dedit.
unā nocte, Paris Helēnam rapuit et ad Trōiam nāvigāvit. Menelaus erat trīstissimus et frātrem quaesīvit. frāter, rēx Agamemnōn, erat potentissimus rēx in Graeciā. Agamemnōn erat rēx Mycēnae.
Menelaus Agamemnōnī omnia narrāvit. Agamemnōn erat iratissimus sed Agamemnōn bellum amāvit. Agamemnōn cōnsilium fēcit.
GRAMMATICA
The imperfect tense: supplemental.
Operatives, as previously noted, the easiest way to translate an imperfect verb is “was verbing.” However, there are other functions of the imperfect that slightly change meaning in order to more accurately convey what type of action is going on. Compare the following:
Continuous action in the past: she was walking / she kept on walking / she used to walk
Attempted action in the past: she tried to walk
Action started in the past: she began to walk
When encountering imperfect verbs, operatives should consider one of the many options available to see if a slightly different meaning increases comprehension.
Additionally, operatives should consider a small feature of Latin verbs. Often the subject will not be named in the sentence. This is especially true if the sentence continues to use the same subject from the previous sentence. For more information about subjectless verbs, please view this video briefing secured from latintutorial.com:
VERBA
| afuit / abest | she/he was absent, away (past tense) / she/he is absent | verb |
| bellum / bellō | war | noun |
| discis | You learn | verb |
| doceō | I teach | verb |
| frater / fratrem | brother | noun |
| legō | I read | verb |
| omnēs | everyone | adjective |
| puella / puellās | girl / girls | noun |
| rēs | thing, affair, matter | noun |
| unus, una | one | adjective |
CULTURALIA
Operative, the Trojan War was the greatest of all myths for both the Greeks and the Romans. The Demiurge advises you to obtain LP bonuses by familiarizing yourself with its parameters, especially the origin of the war.
Achilleus and Odysseus are the heroes of the great homeric epics. Every Roman knew their stories (the Iliad and the Odyssey); you are advised to use those stories in your mission. You should pay close attention to the trick Odysseus and Diomedes pulled off in order to reveal Achilleus' disguise.
ATTUNEMENT
Directions: Using the CULTURALIA section of your CODEX as a guide, answer the following questions:
1. Where was Odysseus king?
2. What were the names of his wife and son?
3. Who were his parents?
4. What was his awesome idea that brought about the fall of Troy?
5. How long was Odysseus away from home?
6. How did Achilles die?
7. Who was Achilles’ mother?
8. Which group did Achilles command?
9. On whose side were Achilles and Odysseus?
10. Which Trojan is credited with being the one who got away and founded Italy?
Directions: The following verbs are given in their first person singular present form. Find another form of each of these verbs in the 4.1 immersion. List the form and translate it correctly for the context in which it is found.
1. salūtō
2. emō
3. discō
4. clāmō
5. vulnerō
6. amō
7. capiō
8. oppugnō
9. parō
10. cēlō
Directions: Copy and paste each sentence into your attunement form, completing it with the correct word in parentheses. Then translate the sentence into English.
1. Agamemnōn Helēnam (vīdit, vidēs, vīdērunt).
2. amīcī lapidem (cēlāvit, cēlāvērunt, cēlābam).
3. nāvēs Graecī (parat, parābant, parābat).
4. meum fratrem Paris (vulnerāvērunt, vulnerāvit, vulnerābant).
5. puellae ad forum (ambulāvit, ambulābat, ambulāvērunt).
6. Tiberius in (sella, sellam, sellā) sedēbat.
7. malus ex (arborem, arbore, arbor) cadit.
8. scīsne tū aliquid dē (Rōmā, Rōma, Rōmam)?
Directions: Match the words in the word bank with the clues.
docet rēs frāter omnēs oppugnavērunt quaesīvit
discis legō vulnerāvit nunc navēs īnsula
1. Stuff, matters, or other business.
2. Sicilia is one. Creta is another.
3. This present time.
4. Menelaus was very sad and ______ his brother.
5. What you do at school.
6. nōn unus.
7. Neptune is Jupiter’s ______.
8. What the Greeks did to Trōia.
9. You might do this with a volūmen.
10. What Paris did to Achilles.
11. The easiest method of transportation from mainland Greece to Troy.
12. What your Agent does.
Directions: Complete the following statements in Latin.
1. salvē. mihi nōmen est ____________________. sum ____________________.
2. Trōiānī sunt inimīcī. debēmus ____________________ eōs.
3. Graecī sunt ____________________. facile est vincere!
4. ubi est Achillēs? eum ____________________.
5. ego tunicam et togam gerō sed Achillēs ____________________ gerit!
6. adsunt multae ____________________ in aulā et inter eās est ____________________.
1. quem deī deaeque ad convīvium nōn invitant?
2. quid Discordia in convīvium iacit?
3. quae deae mālum dēsīderant?
4. secundum Iovem, quis deam pulcherrimam ēligere dēbet?
5. quem Paris ēligit?
6. quid est praemium Paridis?
7. cūr Menelaus est trīstissimus?
8. quis in Graeciā est rēx potentissimus?
9. quid facit Agamemnon?
10. cūr Menelaus tandem est laetus?
11. quī Graecus abest?
12. cūr rēgēs Graecī eum invenīre nōn possunt?